译者按:“海洋连通性工作组”(Marine Connectivity Working Group, MCWG)由世界自然保护联盟世界保护地委员会(IUCN WCPA)设立。其宗旨在于制定基于科学的连通性保护措施,将这些措施有效融入国家、跨领域和全球的海洋保护政策、项目和措施,实现海洋、沿海生态系统和海洋生物的健康和可持续管理。中国生物多样性保护与绿色发展基金会秘书长周晋峰博士目前任“海洋连通性工作组”执委。
近日,绿会国际部收到来自MCWG的最新成果分享,刚刚发布了一份主题为“连接组合效应在稳定海洋保护区方面的作用”(A connectivity portfolio effects stabilises marine reserve performance)的研究报告。在这项研究中,工作组测量了禁捕海洋保护区(鱼类)幼体的分布趋势,表明性能的提高导致幼鱼供应量的波动性增加。然而,海洋保护区体系中鱼类幼体的不同步分布模式产生了显著的组合效应,从而增加了幼体供应的稳定性。现将报告内容摘译如下,以飨读者:
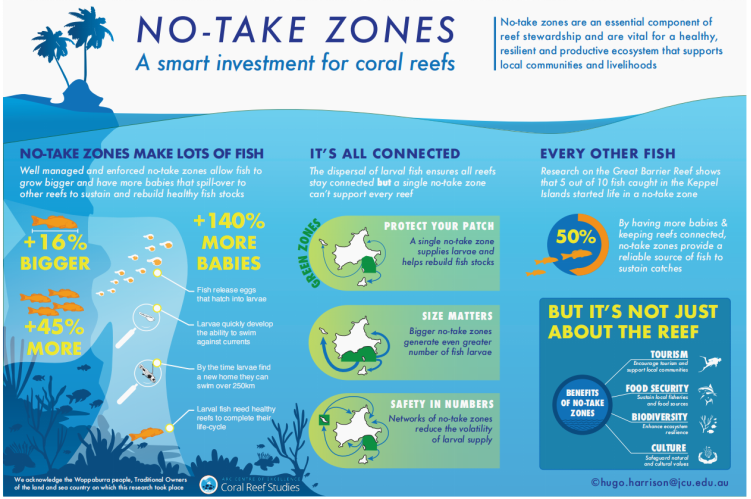
海洋禁捕区内珊瑚礁的利用机制 图源/MCWG, Hugo Harrison@jcu.edu.cn
按+译/JH 审/SY 编/Angel
【研究背景】
Well-managed and enforced no-take marine reserves generate important larval subsidies to neighboring habitats and thereby contribute to the long-term sustainability of fisheries. However, larval dispersal patterns are variable, which leads to temporal fluctuations in the contribution of a single reserve to the replenishment of local populations. Identifying management strategies that mitigate the uncertainty in larval supply will help ensure the stability of recruitment dynamics and minimize the volatility in fishery catches.
良好的管理、强制执行的禁捕海洋保护区为邻近的栖息地提供了重要的鱼苗支持,从而有助于实现渔业的长期可持续性。然而,幼鱼的分布增长模式是不断变化的,这导致单一保护区对补充当地幼鱼的数量值波动较大。降低鱼苗供应不确定性的管理战略将有助于维持动态稳定性,并最大限度地减少渔获量的数值波动。
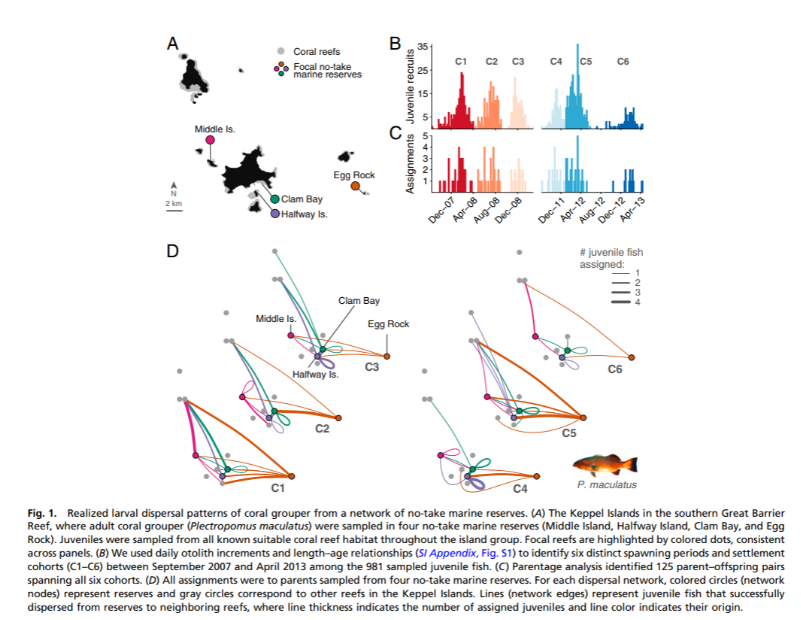
图表ABCD均为MCWG分析保护区(鱼类)幼体分布的可变性时建立的影响分析模型。图源/MCWG
【研究途径】
Here, we use genetic parentage analysis to show extreme variability in both the dispersal patterns and recruitment contribution of four individual marine reserves across six discrete recruitment cohorts for coral grouper (Plectropomus maculatus) on the Great Barrier Reef. Together, however, the asynchronous contributions from multiple reserves create temporal stability in recruitment via a connectivity portfolio effect. This dampening effect reduces the variability in larval supply from individual reserves by a factor of 1.8, which effectively halves the uncertainty in the recruitment contribution of individual reserves. Thus, not only does the network of four marine reserves generate valuable larval subsidies to neighboring habitats, the aggregate effect of individual reserves mitigates temporal fluctuations in dispersal patterns and the replenishment of local populations.
在这里,我们使用遗传亲本分析来研究大堡礁六个离散的珊瑚群中四个海洋保护区的扩散模式和分布补充的极端可变性。然而,来自多个保护区的异步分散样式通过连接性组合效应共同创造了稳定、暂时的种群增长。这种抑制作用将个体保护区幼体分布的可变性降低了1.8倍,有效地将个体保护区补充贡献的不确定性减半。因此,由四个海洋保护区组成的网络不仅为邻近的生境提供了宝贵的鱼苗支持,而且各个保护区的综合效应减轻了扩散模式和当地种群补充的暂时性波动。
【研究结果】
Our results indicate that small networks of marine reserves yield previously unrecognized stabilizing benefits that ensure a consistent larval supply to replenish exploited fish stocks.
我们的结果表明,海洋保护区的网络产生了以前没有被发现的稳定效益,这保证了(鱼类)幼体供应的稳定性,以补充被开发利用掉的鱼类资源。
【研究意义】
Networks of no-take marine reserves support local fisheries by ensuring a consistent supply of juvenile fish. We measured larval dispersal patterns for a highly exploited coral grouper and quantified temporal fluctuations in the recruitment contribution from a network of no-take marine reserves on the Great Barrier Reef. Although recruitment contributions from individual reserves are extremely variable, the reserve network generates a connectivity portfolio effect that successfully dampens the volatility of larval supply to nearby coral reefs. Our findings demonstrate that effective reserve networks can yield previously unrecognized stabilizing benefits that ensure a consistent replenishment of exploited fish stocks.
禁捕海洋保护区网络通过确保幼鱼的持续供应来支持当地渔业。我们测量了一种高度开发的珊瑚石斑鱼的幼体扩散模式,并量化了大堡礁禁捕海洋保护区网络鱼群增量与分布的暂时性波动。虽然单个保护区的补充贡献差异很大,但保护区网络产生了连接组合效应,成功抑制了附近珊瑚礁(鱼类)幼体增长的波动。
报告原文:
A connectivity portfolio effect stabilizes marine reserve performance
https://www.pnas.org/content/117/41/25595
推 荐 阅 读:
接国际专家求助,周晋峰就毛里求斯漏油事件与IUCN海洋连通性工作组探讨并分享康菲溢油案


