On July 25th, the Lop Nur Scientific Expedition Team composed of experts from the comprehensive hydrology team, the plant team and the geological environment team set off from Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Qinghai and other places to meet in Korla, Xinjiang. Organized by the China Biodiversity Conservation and Green Development Foundation (CBCGDF) in 2022, the scientific expedition (Phase 3) to Lop Nur and surrounding areas was launched.
In 2020 and 2021, CBCGDF organized experts in the fields of ecology, hydrology, biology, soil, etc. to go deep into Lop Nur and its surrounding areas, where the experts inspected the three main supply rivers of Lop Nur, the Peacock River, the Tarim River and the Qarqan River Basin. A series of stage investigation results have been obtained on hydrological changes, the distribution of wild terrestrial animal and plant species, the distribution of aquatic organisms, and soil types and distribution characteristics, which have laid a solid foundation for later investigations and comprehensive analysis research.
Recently, the GBIF working group of CBCGDF received the data of Hexinia Polydichotoma (Hexinia polydichotoma (Ostenf.) H. L. Yang) from Lop Nur Scientific Expedition team. The relevant data have been recorded and released on the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) platform for reference and download.
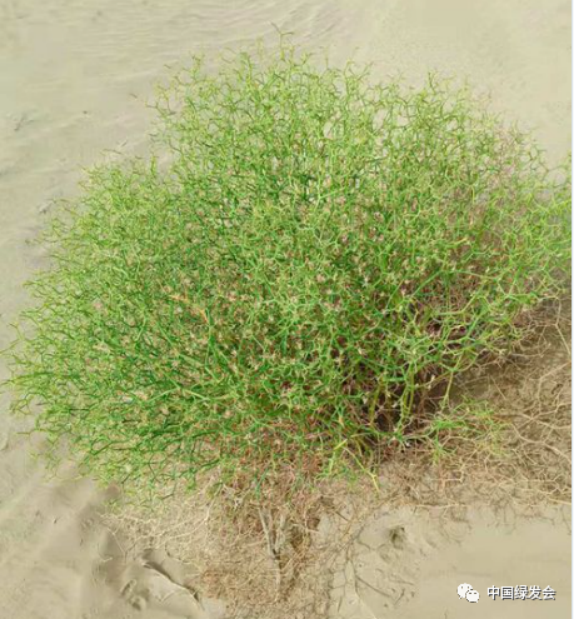

Hexinia polydichotoma (Ostenf.) H. L. Yang was discovered by the Lop Nur Scientific Expedition Team on the Desert Road in Minfeng County on July 27, 2022. Hexinia polydichotoma is a saline plant that grows in sandy areas, lowlands between sand dunes, Gobi ditches and sandy field edges. Because the shape of its branches resembles antlers, it is also called antler grass, which has high ornamental value and is a good ground cover plant and bonsai plant for urban greening in arid areas. Now it is mainly distributed in Gansu and Xinjiang in China. Because of its drought resistance and salinity tolerance, it is widely distributed in the desert areas of Tarim Basin in Xinjiang. It is also an important plant for windproofing and sand fixation, and has important ecological value in the desert fringe.
Citation:https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/3874418316
Zhou J, Wong L (2022). CBCGDF CCAfa Volunteer Observation Archive. Version 1.92. China Biodiversity Conservation and Green Development Foundation. Occurrence dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/wxze8b accessed via GBIF.org on 2022-08-03.
Original Chinese Article: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iQhsIZhXDJP3o-eJgdNHWA
Translator: Sara
Checked by: Lucy
Editor: Lucy
Contact: v10@cbcgdf.org; +8617319454776

Contribution
Do you know? CBCGDF is a non-profit organization. We rely on crowd-funding and donations. You have the opportunity to help us to advance biodiversity conservation. Donate TODAY to power up the movement to make it a better world for all life.
https://www.paypal.me/CBCGDFChina
http://www.cbcgdf.org/English/ConfirmDonaTion/0.html
